Solar PV Panels | Photovoltaic
Solar panels play a crucial role as one of the main components in a solar system, alongside the solar inverter and batteries. Understanding their composition and functionality is essential to fully grasp the potential of solar power.
Photovoltaics: Converting Light into Electricity
Before diving into solar panels, let's shed light on a term you may have encountered during your solar power research: Photovoltaic (PV) or Photovoltaics. It refers to the process of converting light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon, studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry, is commercially harnessed for electricity generation and as photosensors.
At its core, photovoltaics involves the direct conversion of light into electricity at the atomic level. Some materials possess a unique property known as the photoelectric effect, where they absorb photons of light and release electrons. Capturing these free electrons generates an electric current that can be utilized as electricity.
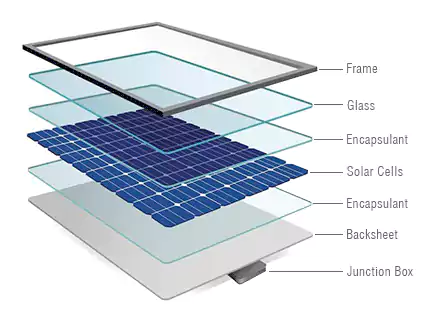
What are Solar Panels made of?
Solar Panels are the building blocks of solar energy. Now, let's delve into the remarkable composition of solar panels. The large, black panels you often spot on homes and businesses consist of multiple solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells. These cells are made of silicon semiconductors, which have the remarkable ability to absorb sunlight and generate an electric current. When these individual cells are interconnected, they form a complete solar panel.
Fast Fact
A fascinating fact about silicon, the main raw material of solar panels, is that it is a nonmetallic chemical element found abundantly in the Earth's crust. In fact, silicon makes up 27.7 percent of the Earth's crust, surpassed only by oxygen. This highly versatile material serves as the foundation for solar panels, while the outer frame enclosing the array of cells is typically made of transparent glass. The transparency of the glass is crucial as it allows sunlight to penetrate the panel and reach the silicon cells.
By weight, approximately 80 percent of a solar panel comprises glass and aluminum, both of which are highly recyclable materials. Additionally, solar panels contain rare elements such as gallium and indium, which can be recovered through recycling processes.
Understanding the Costs
While solar panels offer immense benefits, it's important to acknowledge that they can be relatively costly. This is primarily due to the high-quality materials used in their manufacturing. Pure silicon, a metal, is the predominant component of solar panels, and its production requires a significant amount of energy.
Crystalline silicon, often referred to as "solar grade silicon," is the most widely used material for solar cells. These cells are obtained by slicing thin wafers, approximately 160-240 μm thick, from a single crystal or block of silicon. The type of crystalline cell produced depends on the specific manufacturing process used for the silicon wafers. Monocrystalline cells are among the main types of crystalline cells used in solar panels.
Silicon is an ideal semiconductor material for solar panels due to its cost-efficiency, good energy efficiency, high corrosion resistance, long-term durability, optimal thermal expansion properties, good photoconductivity, and low toxicity.
Embracing the Power of Solar Energy
By understanding the composition and advantages of solar panels, you can appreciate their role in harnessing the sun's energy for clean and renewable power. Solar panels offer a sustainable solution that not only reduces reliance on traditional energy sources but also contributes to environmental well-being. With their exceptional properties and technological advancements, solar panels pave the way toward a brighter, more sustainable future.



